What it is advisable to know
- In 2023, there have been 97 zero-day vulnerabilities exploited, a big rise of over 50% in comparison with 2022 (62 vulnerabilities).
- Evaluation by Google’s Menace Evaluation Group (TAG) and Mandiant revealed that espionage was the first motive behind 48 out of 58 zero-day vulnerabilities analyzed.
- Criminals centered on end-user platforms like smartphones, working programs, net browsers, and functions, with a complete of 61 zero-days affecting these targets.
Google has discovered that there have been 97 zero-day vulnerabilities that had been exploited in 2023, over 50% greater than the quantity from 2022 (62 vulnerabilities).
Google’s Menace Evaluation Group (TAG) and Mandiant teamed as much as analyze the zero-day flaws revealed final yr. Their evaluation revealed that out of the 58 zero-days for which they might attribute the risk actor’s motivations, espionage was the principle motive for 48 of these vulnerabilities.
Zero-days are primarily flaws that have not been discovered by safety specialists but. This implies IT groups have zero time to repair them earlier than hackers exploit them. That is why hackers love them, as a result of utilizing them does not set off any alarms.
Out of all of the potential targets, criminals had their sights set on end-user platforms and merchandise like smartphones, working programs, net browsers, and varied functions. Google discovered {that a} complete of 61 zero-days impacted these targets.
In 2023, Android noticed 9 vulnerabilities being exploited, up from simply three in 2022. Then again, iOS confronted 9 zero-days out within the wild, in comparison with 4 within the earlier yr.
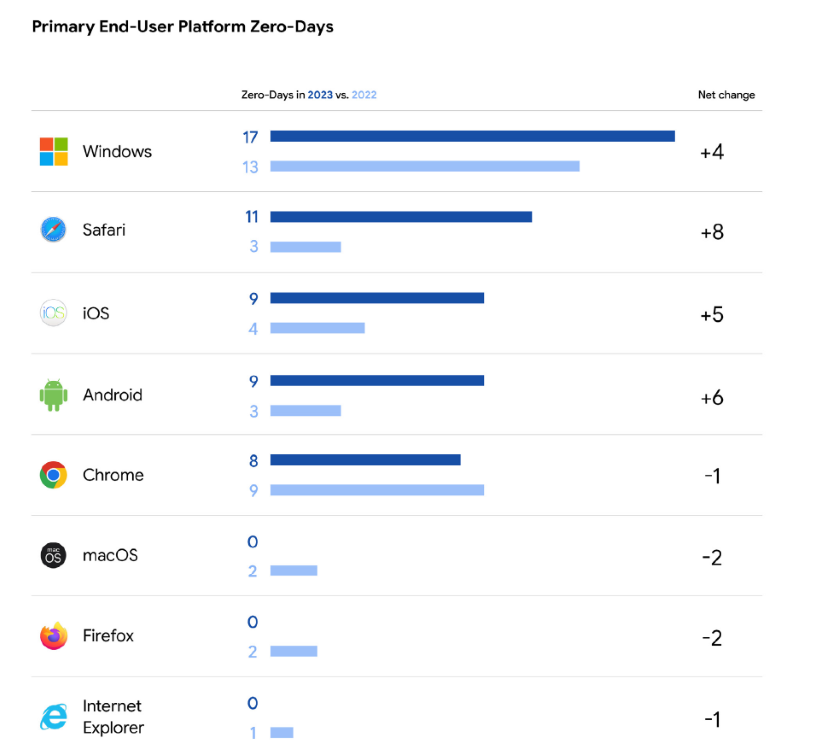
Moreover, there have been eight zero-days hitting Chrome and 11 focusing on Safari within the wild. Home windows takes the lead among the many high 5, with 17 zero-day vulnerabilities exploited, up from 13 the earlier yr.
Wanting on the findings by area, Google stories that 12 of the zero-days had been exploited by Chinese language state-sponsored risk actors, with Russia, North Korea, and Belarus following swimsuit. In complete, state-sponsored espionage made up 41.4% of the exploited zero-days in 2023.
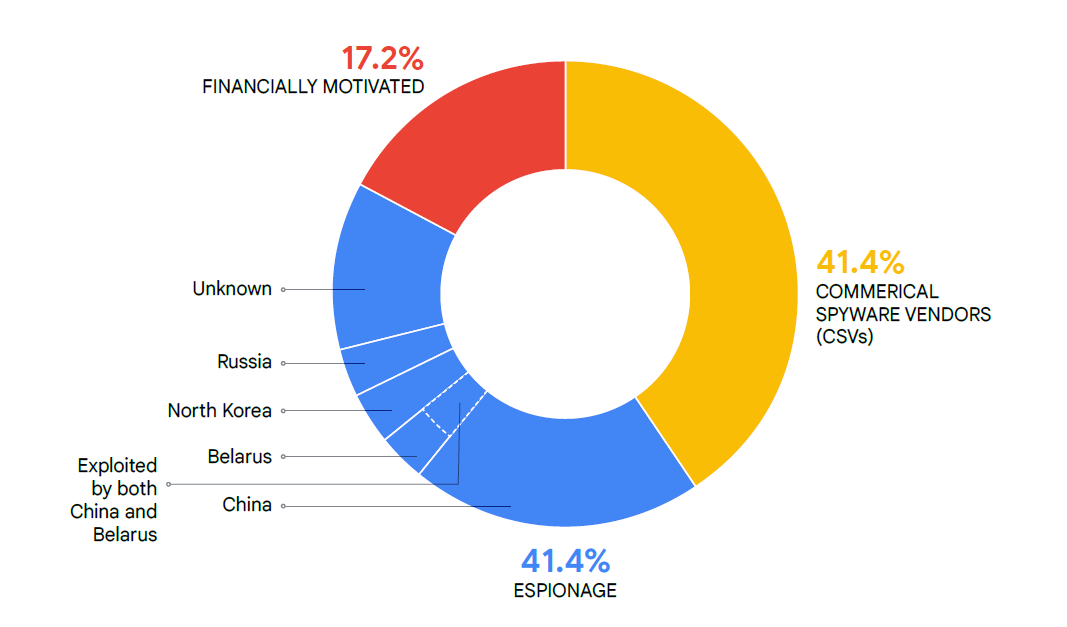
“In 2023, we attributed to business surveillance distributors (CSVs) and authorities espionage actors a mixed 48 of 58 zero-days for which we might attribute motivation and solely 10 vulnerabilities to financially motivated actors,” Google says. “The proportion (roughly 17%) in 2023 of financially motivated exploitation is barely decrease than our observations from 2022, and each of those years had been down from the almost one-third of vulnerabilities we attributed to financially motivated actors in 2021.”
That mentioned, investments in exploit mitigations throughout browsers and working programs are making it tougher for attackers to realize their targets utilizing sure sorts of vulnerabilities.
Google’s researchers level out that firms like Apple, Google, and Microsoft, who’re accountable for end-user platforms, have made important investments. These investments are clearly affecting the categories and amount of zero-days that attackers can exploit.
Anyway, 2023 noticed fewer disclosed zero-day flaws than 2021, which had 106 vulnerabilities. Whereas this would possibly sound like factor, researchers assume that the speed of zero-day discovery and exploitation will most likely keep excessive in comparison with the numbers earlier than 2021.


